Solar Decathlon 2023 Studio - Industrialized Construction

Solar Decathlon has long been synonymous with digestible building science education. Now, the competition is launching a new initiative—SD Studio—to feature one cutting-edge building topic in depth each academic year. The 2022/2023 topic is industrialized construction.
Industrialized production methods—such as high-volume off-site construction, prefabrication, and on-site construction automation—can be used to construct or retrofit buildings, often leading to reduced costs and the potential for increased energy efficiency and decarbonization.
Industrialized construction techniques can be applied to Solar Decathlon Design Challenge or Build Challenge projects. The FAQ section below aims to orient current Solar Decathlon teams to industrialized construction basics and provide resources for additional information.
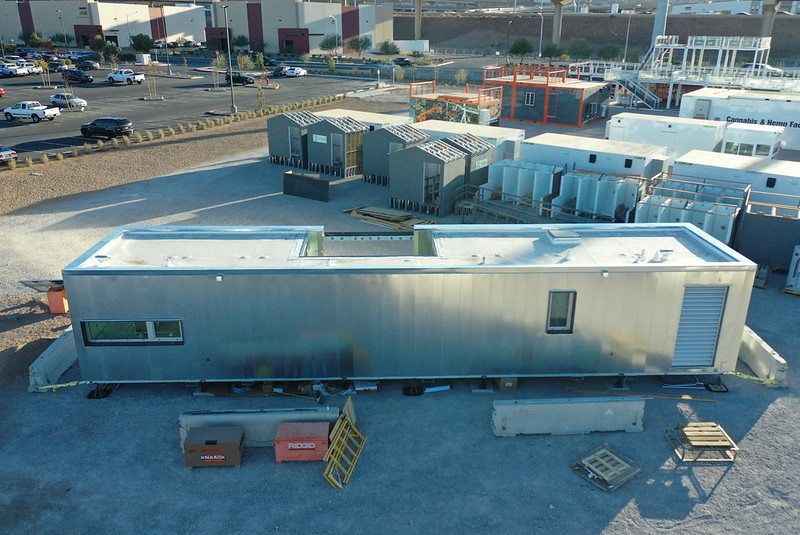

Off-site, modular construction for the University of Nevada, Las Vegas 2020 Build Challenge team.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is industrialized construction?
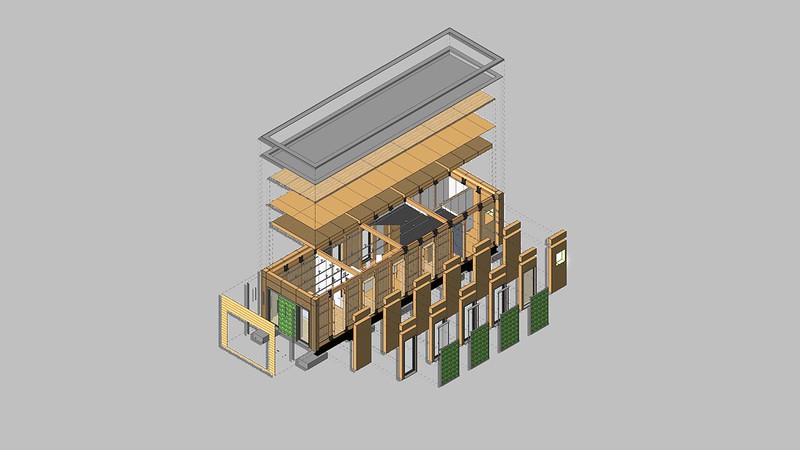
- Industrialized construction applies industrial production methods from the manufacturing industry to the traditional building construction system. Some examples of industrialized construction methods are off-site construction, prefabrication, and modularization.
- These methods can help increase construction productivity, which is lower today than it was in the 1960s.
- Industrialized construction can also improve the quality of construction through more stringent factory inspections and the use of components that increase energy efficiency.
- Learn more: Production Control Through Modularisation.
What is off-site construction?
- Off-site construction is the planning, design, fabrication, and assembly of building elements at a site other than their final installed location to support the rapid and efficient construction of a permanent structure. Off-site construction uses integrated planning and supply chain optimization strategies.
- Off-site construction may take place at permanent off-site factories or at "flying factories," temporary facilities that are created only for the duration of the project before "flying" to another location for the next project.
Off-Site Construction FAQs (International Code Council)
What is prefabrication?
- Prefabrication is a manufacturing process, generally taking place at a specialized facility, in which various materials are joined to form a component part of a final installation. Prefabricated components can be assembled more quickly at their intended site after manufacture. This allows for a variety of benefits such as a reduction in delays due to extreme weather, allowing for specialized work of a single skilled trade, and reducing the time workers may need to travel to remote sites.
What is modular construction?
- Modular construction is a process in which a building is constructed off-site, under controlled factory conditions, using the same materials and designing to the same codes and standards as conventionally built facilities—but in about half the time. Buildings are produced in "modules" that when put together on-site reflect the identical design intent and specifications of the most sophisticated site-built facility.
- Modular construction projects are typically built to near completion off-site, while other industrialized construction techniques may only build parts of the whole off-site.
Are there different types of modular buildings?
- There are two main
types of
modular buildings.
- Re-locatable modular, also called "temporary modular," are structures that meet temporary needs. These buildings can be leased or purchased and may not meet the same code standards as permanent buildings. Examples include job site trailers, temporary classrooms, and show rooms, to name a few.
- Permanent modular construction structures are comparable to site-built structures and must meet International Building Code (IBC) standards. The only difference between permanent modular construction and traditional on-site construction is that the modular structure is manufactured in segments in a factory before being transported to the site. Permanent modular construction is used for multistory structures, single family homes, health care facilities, schools, hotels, and any other building types found in traditional on-site construction.
What codes govern off-site and modular construction?
In 2021, the International Code Council (ICC) and the Modular Building Institute (MBI) published two new comprehensive standards related to off-site and modular construction.
- ICC/MBI Standard 1200-2021 focuses on processes such as planning, designing, fabricating, transporting, and assembling commercial and residential building elements, including componentized, panelized, and modularized elements.
- ICC/MBI Standard 1205-2021 focuses on the inspection, approval and regulatory compliance of off-site residential and commercial construction components, and their assembly and completion at the final building site. Topics addressed include permitting, in-plant and on-site final inspections, third-party inspections, state modular programs, and the authority having jurisdiction.
What organizations provide more information about off-site and modular construction?
- The Off-Site Construction Council (OSCC) was established in 2013 by the National Institute of Building Sciences to serve as a research, education, and outreach center for information on off-site design and construction for commercial, institutional, and multifamily facilities.
- The Modular Building Institute was founded in 1983 as an international nonprofit trade association serving modular construction.
Exterior rendering of the modular “Celsius House” from the Hogeschool Utrecht University of Applied Sciences team in the 2020 Build Challenge.
Getting Started with Industrialized Construction
WATCH: Industrialized Construction Innovation at NREL
Key Readings:
- Off-site and Modular Construction Explained (Whole Building Design Guide)
- A Preliminary Overview of Emerging Trends for Industrialized Construction in the United States (Stanford University)
- Scaling Up Off-Site Construction in Southern California (Terner Center for Housing Innovation, University of California, Berkley)
- Off-Site Construction in Los Angeles County (Terner Center for Housing Innovation, University of California, Berkley)
- Modular Manufacturing in Multifamily Housing (Terner Center for Housing Innovation, University of California, Berkley)
- Industrialized Construction Innovation (National Renewable Energy Laboratory)

Students construct a modular, zero energy home.
Related Industrialized Construction Resources
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly
- Design for X: Concurrent engineering imperatives (Chapman & Hall)
- Design for Manufacture and Assembly (Designing Buildings Ltd)
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Integration
- The Energy in Modular (EMOD) Building Method: A Guide to Energy-Efficient Design for Industrialized Construction of Modular Buildings (NREL)
- The Potential of Prefab: How Modular Construction Can Be Green (Building Green)
- Prefabrication and Modularization (McGraw-Hill Construction)
Low Embodied Carbon and Waste Reduction
- Construction Matters: Comparing Environmental Impacts of Building Modular and Conventional Homes in the United States (Journal of Industrial Ecology)
- Decarbonization During Predevelopment of Modular Building Solutions (National Renewable Energy Laboratory)
